Negative Calorie Diet Review
This is a hard diet plan to plan and accomplish. Even if you want to, it has to be thought about and this can take a bit of time to set up a negative calorie diet plan. A negative diet plan is one that provides less food calories than what you need to digest them. If you find this first part confusing, then this diet is going to be frustrating. This is one big disadvantage to the negative calorie diet plan.Some foods allowable in this plan are broccoli, apples, beets, asparagus and cauliflower to name a few. These are not any negative foods, because there is know such thing as a negative calorie food. But there are foods outlined in the negative diet plan. The diet itself is not a realistic diet because these foods are healthy and do not help you lose weight.

Basic calories do not burn calories. The only way to burn calories is to exercise and take in the recommended daily calories needed. So with this in mind, you can choose this plan if you feel this will be a positive diet plan for you or whether it will be a negative one. You will find out that the way to burns calories is to exercise, not eat foods that add calories instead of burning them.
You don’t want to be fooled into thinking you are burning calories by eating such foods when in turn these foods are adding calories to your diet. This will add weight gain if you do not participate in an exercise routine. There is no such evidence of a negative food to burn bad calories. It is a myth that cannot be substantiated by anyone. This will cause concern when you are considering a negative calorie diet plan.
Fruits and vegetables do contain calories, but they are considered healthy calories verses junk foods that produce negative calories. So if you get rid of the bad calories and just eat the good calorie foods, you will stay healthy. Losing weight will need to include exercise and proper eating habits.
So is the negative calorie diet plan a reality, I don’t believe so. I have found no information to back up a positive result. The information provided has not proved that there is such a diet like this that contributes to weight loss. Be leery of plans that say you can lose weight by eating negative calorie foods, as this has not been proven.
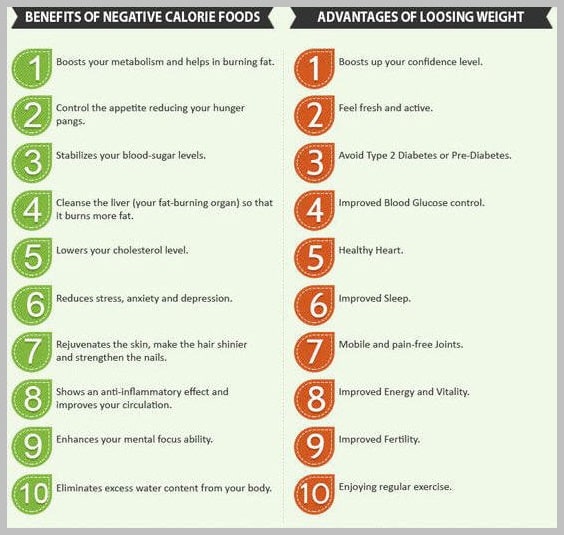
With this said, you may be wondering what types of Negative Calorie Diet foods I am referring to.
Below you will find such a list:

Here are some foods that are often considered low in calories and nutrient-dense:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, lettuce, and other leafy greens are high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber while being low in calories.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage are rich in fiber and nutrients while being relatively low in calories.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are not only low in calories but also packed with antioxidants and vitamins.
- Cucumbers: These have a high water content, contributing to hydration, and are low in calories.
- Celery: Often touted as a negative calorie food, celery is low in calories and provides some fiber.
- Watermelon: With high water content, watermelon can be a refreshing, low-calorie snack.
- Carrots: Carrots are crunchy, low-calorie vegetables that provide beta-carotene and fiber.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are rich in vitamins and antioxidants and can be included in salads or eaten as snacks.
- Bell Peppers: Low in calories and high in vitamin C, bell peppers are versatile and can be added to various dishes.
- Zucchini: This low-calorie vegetable can be used in a variety of recipes, from spiralized “zoodles” to grilled slices.
Remember, while incorporating these foods, it’s crucial to maintain a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure you’re meeting your body’s nutritional needs.
| Negative Calorie Vegetables | Negative Calorie Fruits |
| Asparagus Beet Broccoli Green Cabbage Carrot Cauliflower Celeriac also know as celery root Celery Chicory Chili Peppers Cucumber Dandelion Endive Garden Cress Garlic Green Beans Lettuce Onion Papaya Radishes Spinach Turnip Zucchini | Apple Blueberry Cantaloupe Cranberry Grape Fruit Honey Dew Melon Lemon Mango Lime Orange Peach Pineapple Rasberry Strawberry Watermelon |
[content-egg-block template=top_listing]
A Critical Look at the Negative Calorie Diet: Separating Fact from Fiction
The Negative Calorie Diet has gained popularity in recent years, promising a unique approach to weight loss by emphasizing the consumption of foods that supposedly burn more calories during digestion than they contribute. While the concept may sound enticing, it’s essential to critically examine the scientific validity and practicality of such a diet.
One of the core principles of the Negative Calorie Diet is the idea that certain foods, often low-calorie fruits and vegetables, require more energy to digest than they provide, resulting in a net caloric loss. While it is true that the thermic effect of food (TEF) contributes to caloric expenditure during digestion, the extent to which specific foods can trigger a negative calorie balance is questionable.
The diet primarily encourages the consumption of foods like celery, cucumbers, and berries, emphasizing their low-calorie content and high fiber levels. Proponents argue that the digestive process of breaking down these foods burns more calories than the foods themselves contain. However, scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited, and the overall impact on weight loss is likely to be marginal.
Furthermore, the Negative Calorie Diet may pose practical challenges for individuals seeking a sustainable and balanced approach to nutrition. Relying solely on low-calorie foods may lead to nutritional deficiencies, as these foods might not provide all the essential nutrients the body needs for optimal functioning.
It’s crucial to approach any diet with caution, and the Negative Calorie Diet is no exception. Weight loss is a complex process influenced by various factors, including calorie intake, physical activity, metabolism, and individual differences. Adopting a well-rounded and evidence-based approach to nutrition, such as maintaining a calorie deficit through a balanced diet and regular exercise, remains a more reliable strategy for long-term weight management.
In conclusion, the Negative Calorie Diet’s premise of consuming foods that purportedly burn more calories during digestion than they provide lacks robust scientific support. As with any diet, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals or nutrition experts before making significant changes to your eating habits. Choosing a sustainable and balanced approach to weight loss is key for achieving lasting results and overall well-being.





